Understanding Osteogenesis Imperfecta ( Brittle Bone Disease )
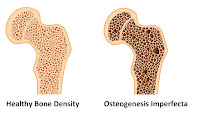
Osteogenesis imperfecta is one of the bone diseases due to genetic disorders. This disorder causes brittle bones and fractures readily, even in the absence of impact. This disorder is quite rare and is generally inherited from both parents.
Diagnosis of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
To determine the
diagnosis of imperfect osteogenesis disease,
the doctor will conduct detailed medical interviews, physical examinations, and
other supporting examinations.
People with osteogenesis imperfect generally
experience fractures that can often even occur up to hundreds of times each
year. Fractures can occur in any area of the body, both long bones and small bones.
The medical interview and physical examination were then confirmed by DNA research in the laboratory. Ninety percent of DNA testing results of patients with osteogenesis show the presence of a type 1 collagen mutation. Collagen itself is the main structure of bone formation. If this collagen is abnormal, the bone density will be sacrificed,
making it easy to break.
Although this DNA
test is a confirmatory examination, a negative result does not necessarily rule
out the possibility of imperfect osteogenesis. It could be that the case that
occurs remains osteogenesis imperfect; it's just that the mutation that happens is
not detected. Or another possibility is that the patient has osteogenesis
flawed type recessive mutation. No abnormalities were found in type 1 collagen
DNA in recessive mutations, but disturbances occurred in collagen production
itself.
Causes of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfections are caused by genetic abnormalities of
collagen, the main structure of bone formation. In osteogenesis imperfect, the
dominant mutation type, this genetic disorder occurs in collagen type 1.
The type 1
collagen produced is abnormal, so the bones become brittle and easily broken.
While in recessive mutations, abnormalities occur in the collagen production
process. Most cases of osteogenesis
imperfect that arise include the dominant mutation type, about 85–90
percent; the rest are recessive mutation types.
Symptoms of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenesis
imperfect itself has eight types that are distinguished from the kind of
mutation. Type I-IV is a type of genetic mutation of the domain that causes
type 1 collagen abnormalities. Types V and VI are not yet known where the
transformation is known. Meanwhile, types VII and VIII are types of recessive
genetic mutations that disrupt collagen production itself. Each of these types
has symptoms that are different from each other.
Osteogenesis imperfect type I
Some of the
symptoms and signs that appear in this type include:
- The most common and relatively mild
type of osteogenesis imperfect
- Bones are very easily broken and
generally occur before puberty.
- Posture looks normal
- Joints are not sturdy, and muscles
experience weakness
- On the whites of the eyes, there are
blue, purple or gray dots.
- Triangular-shaped face
- Bone abnormalities that occur at least
or not at all
- Sometimes with fragile teeth.
- In some cases, hearing loss is found,
especially at the age of 20-30 years.
- Collagen structure is standard but less
than normal
Osteogenesis imperfect type II
Signs to watch
out for include:
- The heaviest type
- Generally causes death shortly after
birth due to respiratory failure
- Fractures are prevalent and cause
severe bone deformities.
- Short posture with a not perfectly
developed lung
- There are patches of color on the
whites of the eyes.
- Collagen is not perfectly formed.
Osteogenesis imperfect type III
Some of the
symptoms and signs that appear in this type include:
- Bones break easily. Fractures can
occur at birth, and an X-ray image can indicate the healing process of the
bone before birth.
- Short posture
- The whites of the eyes have blue,
purple or gray patches
- Joints are not sturdy, and muscles
are weak, especially in the hands and feet
- Barrel-shaped chest
- Triangular face
- There may be respiratory distress.
- There are bone deformities, generally
severe.
- In some cases, fragile teeth are also
found.
- In some cases, hearing loss is found.
- Collagen structure is not perfectly
formed
Osteogenesis imperfect type IV
Signs to watch
out for include:
- The severity of the disease is
between types I and III.
- Bones are very easily broken and
generally occur before puberty.
- Posture looks shorter than its peers.
- No abnormalities were found in the
whites of the eyes.
- Bone abnormalities that occur at
least or not at all
- Triangular-shaped face
- Barrel-shaped chest
- Sometimes with fragile teeth.
- In some cases, hearing loss is found.
- The collagen structure is not perfectly
formed.
Osteogenesis imperfect type V
Some of the
symptoms and signs that appear in this type include:
- Clinically resembling type IV
- Found images of thick bands on bone
X-rays, especially in long bone growth plates
- There is an abnormal formation of
callus in the area that has broken
- Calcification occurs in the layer
between the radius and ulna
- The whites of normal eyes
- Normal teeth
- Examination of bones under a
microscope shows a picture like a net
- The dominant type of disorder
Osteogenesis imperfect type VI
Signs to watch
out for include:
- Clinically resembling type IV
- The production of alkaline
phosphatase (an enzyme that plays a role in bone formation) has increased.
This is known from blood tests.
- Image of bones under a microscope
looks like fish scales
- Diagnosed from a bone biopsy
- The type of genetic inheritance is
not yet specified whether it is dominant or recessive. But experts strongly
suspect the recessive type.
Osteogenesis imperfect type VII
Some of the
symptoms and signs that appear in this type include:
- Clinically resembling type IV
- Some cases reach type II, which
causes death shortly after birth.
- Short stature
- Short arm and thigh bones
- Coxa vera occurs, which is a change
in the shape of the head of the femur so that it affects the pelvis.
- There is a recessive mutation of the
CRTAP gene(Cartilage- AssociatedProtein)
Osteogenesis imperfect tipe VIII
Signs to watch
out for include:
- It clinically resembles type II or
type III, which causes death shortly after birth.
- Impaired growth with heavy intensity
- Bone mineralization is severely
impaired.
- There is a deficiency of P3H1(Prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1)due to
lepre1 gene mutation.
Treatment of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Until now, there
has been no treatment that can totally cure patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. Treatment is more intended to improve the
quality of life of sufferers. Fractures are treated with surgery, both small
and large, physiotherapy, and use a walker or wheelchair if necessary.
In addition,
hormone therapy using growth hormone, drugs and gene therapy is often used in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta.
In addition to
medical treatment, exercise and nutritional regulation of patients with osteogenesis imperfecta are also no
less important. The recommended sport is a low-impact sport such as swimming or walking. This type of exercise
can minimize the potential for fractures and help increase bone and muscle
strength.
In addition, patients
with osteogenesis imperfecta are also
expected to maintain a healthy lifestyle by not smoking, drinking alcoholic
beverages, consuming caffeine in excess, and avoiding steroid drugs. All of
these things can reduce bone density and aggravate the risk of fractures.
Complications of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Various
complications can occur in patients with
osteogenesis imperfecta. The
severity of complications depends on the severity of clinical symptoms.
The most severe
complication is respiratory failure that leads to death. In addition, the
psychological condition of the sufferer is also often the second victim after
his bones. Limited activity the short posture often make sufferers low
self-esteem and do not have an optimal life. Depression is the threat of
psychic complications that should not also be ruled out.
Prevention of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenesis
imperfecta is an unavoidable disease. Preventive measures are more aimed at
minimizing the risk of fractures. This prevention is done by maintaining a
healthy lifestyle and choosing various activities classified as safe to do.